Myopia (Nearsightedness)
Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
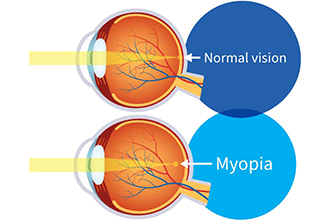
Myopia, commonly known as nearsightedness, is a refractive error of the eye. In myopia, distant objects appear blurry, while close-up objects can be seen clearly. This condition occurs when the eyeball is too long or the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye) is too curved. As a result, light entering the eye focuses in front of the retina instead of directly on it.
At Nandadeep Eye Hospital, we have setup a first of its kind Myopia Clinic in southern Maharashtra. We offer personalized care for patients with myopia. Our experienced optometrists and ophthalmologists provide comprehensive assessments, accurate prescriptions, and evidence-based treatments.
Myopia Treatment for Children and Teens
Are you worried about increasing your child’s minus number (Myopia)? Myopia (short-sightedness) is becoming more common among children in India, affecting their ability to see distant objects clearly. Left untreated, it can worsen over time and lead to serious eye problems like cataracts, glaucoma, lazy eye (amblyopia), and retinal complications in the future. At Nandadeep Eye Hospital, we specialize in myopia treatment for children and teens and offer practical solutions to slow down the progression of myopia and protect your child’s vision.
As myopia progresses, it not only affects your child’s ability to see distant objects but can also impact their academic performance, social interactions, and overall well-being. The earlier myopia is detected and managed, the more effective the treatment will be in slowing down its progression. Without proper intervention, children with high myopia are at an increased risk of developing serious eye complications later in life. That’s why early management is critical. We offer comprehensive eye care solutions specifically designed to address myopia in children, helping protect their vision and ensure a brighter, clearer future.
Myopia Treatment Options for Children
1. Specialty Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses
- Multifocal lenses: Designed to correct myopia and improve focus on distant objects.
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K): Special contact lenses worn overnight to reshape the cornea and provide clear vision during the day.
2. Atropine Eye Drops
Low-dose atropine eye drops are one of the most effective ways to control myopia progression in children. These drops relax the eye muscles, reducing the strain that leads to worsening myopia.
3. Lifestyle Changes and Vision Therapy
Encouraging outdoor play and limiting screen time can help slow down the increase of the minus number. Vision therapy exercises, supervised by a specialist, can also train the eyes to focus better and improve visual skills.
Why Is My Child’s Minus Number Increasing?
- Excessive screen time
- Lack of outdoor activities
- Genetics
- Improper lighting while reading or studying

Myopia can be caused by
- Axial Myopia: Increase in diameter of the eyeball
- Curvature Myopia: Due to increase in curvature of cornea, lens or both
- Positional myopia: Due to anterior placement of crystalline lens
- Index myopia: Due to increase in refractive index of media
Myopic progression
Myopic progression refers to the gradual worsening of nearsightedness (myopia) over time.
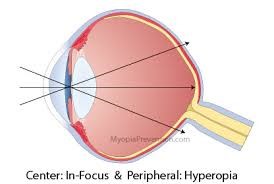
It is caused by something known as peripheral defocus, it refers to the blurry focus of light rays that fall on the outer edges of the retina (the peripheral retina) rather than on the central fovea. This phenomenon occurs primarily in myopic eyes, which have an elongated shape. When light rays focus behind the retina in the peripheral area, biochemical signals are triggered, leading to further elongation of the eye. This elongation contributes to the progression of myopia, where distant objects appear blurry due to the altered eye shape.
Why Progressive Myopia Is a Concern
Continual Progression:
- Some children who develop myopia experience a continual progression of their nearsightedness. They require higher eyeglass prescriptions year after year. This phenomenon, known as progressive myopia, typically begins in early childhood. Research indicates that the younger a child develops myopia, the faster their myopia can progress.
Global Prevalence:
- Myopia is one of the most common eye disorders worldwide. In Europe and the United States, approximately 30% to 40% of adults are nearsighted. However, in several East Asian countries, up to 80% or more of adults have myopia. Researchers estimate that roughly half of the world’s population will have myopia by the year 2050.

Classification of Myopia Severity:
- Low Myopia: Ranges from -0.50 D to -2.75D
- Moderate Myopia: Ranges from -3.00D to -5.75 D.
- High Myopia: Begins at -6.00 D and greater. Having any degree of myopia increases the risk of complications later in life, but the likelihood of complications rises significantly as myopia progresses. People with progressive myopia and high myopia face a much higher risk of complications than those with low or no myopia.
Eye Problems Associated with High Myopia:
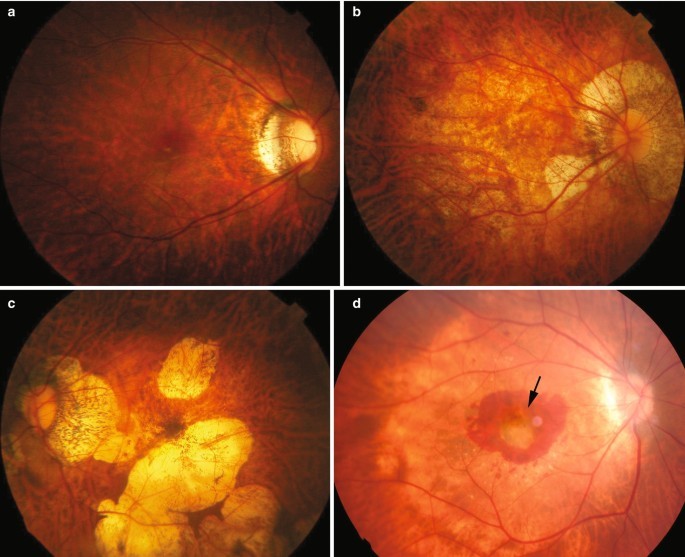
- Myopic Maculopathy: Also known as myopic macular degeneration, this condition becomes more likely as the degree of myopia increases. The risk for myopic maculopathy is significantly higher in people with high myopia. It can lead to irreversible vision loss.
Why Progressive Myopia Is a Concern
1. Continual Progression
Some children who develop myopia experience a continual progression of their nearsightedness. They require higher eyeglass prescriptions year after year. This phenomenon, known as progressive myopia, typically begins in early childhood. Research indicates that the younger a child develops myopia, the faster their myopia can progress.
2. Global Prevalence
Myopia is one of the most common eye disorders worldwide. In Europe and the United States, approximately 30% to 40% of adults are nearsighted. However, in several East Asian countries, up to 80% or more of adults have myopia. Researchers estimate that roughly half of the world’s population will have myopia by the year 2050.

3. Classification of Myopia Severity
- Low Myopia: Ranges from -0.50 D to -2.75D
- Moderate Myopia: Ranges from -3.00D to -5.75 D.
- High Myopia: Begins at -6.00 D and greater. Having any degree of myopia increases the risk of complications later in life, but the likelihood of complications rises significantly as myopia progresses. People with progressive myopia and high myopia face a much higher risk of complications than those with low or no myopia.

4. Eye Problems Associated with High Myopia
- Myopic Maculopathy: Also known as myopic macular degeneration, this condition becomes more likely as the degree of myopia increases. The risk for myopic maculopathy is significantly higher in people with high myopia. It can lead to irreversible vision loss.
Managing Progressive Myopia
Nandadeep Refractive Surgery Centre distinguishes itself from other hospitals in Southern Maharashtra with several unique features:
Regular Eye Exams
Annual eye exams are essential to monitor myopia progression and adjust prescriptions as needed.

Outdoor Time
Encourage children to spend time outdoors, as it may help slow myopia progression.
Myopia Control
Various methods, such as orthokeratology (ortho-k) contact lenses, atropine eye drops, and multifocal soft contact lenses, can help slow down myopia progression.
Signs and Symptoms of Progressive Myopia
- Blurry Distance Vision: Distant objects appear unclear.
- Eyestrain: Frequent eye strain, especially during activities like reading or using digital screens.
- Headaches: Persistent headaches, often related to visual tasks.
- Squinting: Excessive squinting to see distant objects clearly.
- Difficulty Driving at Night: Myopia can worsen night vision.
- Changing Prescription: Frequent changes in glasses or contact lens prescriptions.
Instruments in our clinic
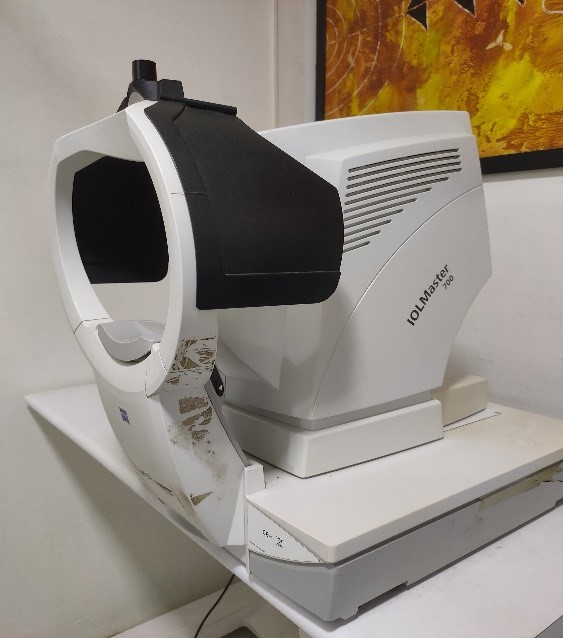
IOLMaster
In myopia clinics, the IOLMaster helps determine the change in the length of the eye ball also helps to keep track if there is any progression of length.
Fundus Camera
A fundus camera captures detailed images of the retina, which is the back portion of the eye. It helps to check if myopia is affecting the integrity of the retina.
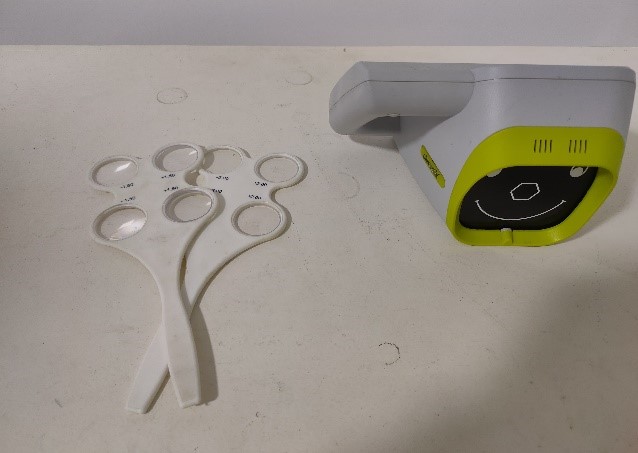

Plusoptix
Used for detecting refractive errors (myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism) in children. And to monitor the changes in the power of the eye.
Pentacam (Corneal Tomography)
The Pentacam provides comprehensive corneal tomography, assessing both anterior and posterior corneal surfaces.
Treatment Options for Progressive Myopia

Peripheral Defocus Spectacles
These specialized eyeglasses are designed to alter peripheral retinal defocus. The central portion corrects the refractive error, while the surrounding peripheral zone provides a different focus.
Atropine
Low-dose atropine eye drops (0.01%) have shown promise in slowing myopia progression.

Outdoor Activities
Spending time outdoors has a protective effect against myopia development. Exposure to natural light, even in shaded areas, may be sufficient to slow myopia progression.

Reducing Screen Time
Prolonged screen time, especially close-up activities like reading or using digital devices, can strain the eyes and contribute to myopia progression.
Our Myopia Experts
Dr. Sourabh D. Patwardhan
Phaco-Refractive-Vitreoretina- Glaucoma specialist FRCS (UK), MS (AIIMS), DNB, MNAMS, FICO

Optom Sayan Mukherjee
B.Optom., M. Optom. Consultant Optometrist, Vision Therapy, Speciality Contact lens